Degradable materials for coffee packaging are a sustainable and environmentally friendly option to consider. They can help reduce the environmental impact of single-use coffee packaging. Some options for degradable materials in coffee packaging include:
Biodegradable plastics like PLA (polylactic acid) and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) are derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. These materials break down into natural components over time when exposed to the right conditions, such as high temperatures and microbial activity.
Biodegradable plastics are a category of materials with significant environmental potential, as they naturally degrade under specific conditions, reducing their impact on the environment. Here is a more detailed overview of biodegradable plastics:
Types and Composition: Biodegradable plastics include various types, with the most common being polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), polycaprolactone (PCL), and more. These materials are typically derived from biomass sources like corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose, rather than petroleum, making them a subset of bioplastics. This results in lower greenhouse gas emissions throughout their lifecycle, making them more environmentally friendly compared to traditional plastics.
Biodegradation Process: Biodegradable plastics break down into natural components under specific conditions, which typically include high temperatures, humidity, exposure to light, and microbial activity. Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi grow on the surface of biodegradable plastics, breaking molecular bonds and converting them into carbohydrates, water, and carbon dioxide. This process resembles natural organic matter decomposition in the environment.
In summary, biodegradable plastics represent a promising solution to mitigate plastic pollution and reduce dependence on limited resources. However, their effectiveness depends on various factors, including degradation rate, environmental conditions, and the availability of recycling and composting infrastructure, ensuring that they achieve their environmental goals.
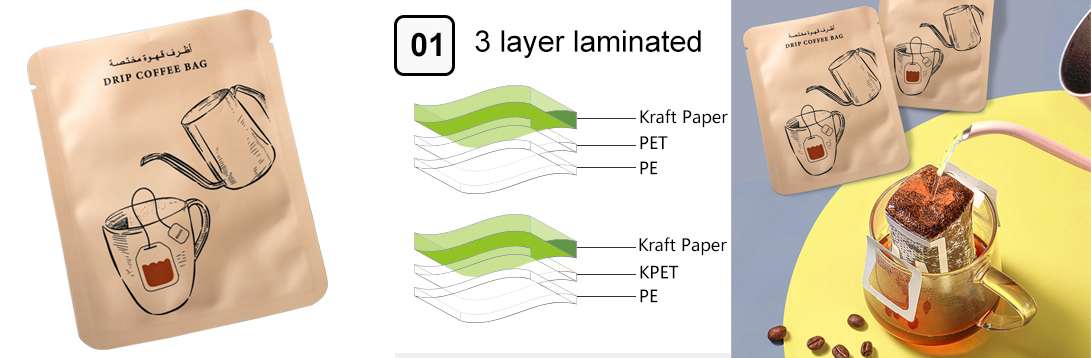
Traditional paper and cardboard packaging are biodegradable and compostable. Look for options with minimal or no plastic coatings to ensure faster decomposition.
Paper and cardboard are traditional and widely used materials for packaging, known for their biodegradability and recyclability. Here's a detailed overview of their use in various packaging applications:
Paper: Paper is made from wood pulp, which can be sourced from sustainably managed forests. It's a renewable resource, and the paper-making process can be environmentally friendly when managed properly.
Cardboard: Cardboard is a thicker and more rigid material than paper. It is often used for packaging boxes and cartons. Cardboard can be made from paper pulp and may contain recycled content.
Paper and cardboard are inherently biodegradable materials. They break down naturally over time, returning to the environment as organic matter. This makes them an environmentally friendly choice, as they do not contribute to long-lasting waste or pollution.
We use eco-friendly printing methods for paper and cardboard packaging. This includes using soy-based inks, which are more environmentally friendly than traditional petroleum-based inks.
Biodegradability and recyclability: Paper and cardboard are easily recyclable and biodegradable, reducing their environmental impact.
Sustainable sourcing: Many paper products are made from sustainably managed forests, which helps conserve natural resources.
Versatility: These materials can be easily customized through printing and branding, making them suitable for a wide range of packaging needs.
Lightweight: Paper and cardboard are lightweight materials, which can help reduce transportation costs and emissions.
Compostable Packaging:
Compostable materials, such as certified compostable plastics or packaging made from compostable plant-based materials like cornstarch or sugarcane, can be a good choice. These materials break down into non-toxic, organic matter when subjected to the conditions found in industrial composting facilities.
Bio-Based Films: 
Packaging films made from bio-based materials, such as cellulose, starch, or algae, can be biodegradable or compostable, depending on their composition. These materials are often renewable and have a lower environmental impact.
Recycled Materials:
Using recycled materials for coffee packaging, such as recycled paper or cardboard, can reduce the need for new resources and contribute to a more sustainable packaging option.
Edible Packaging:
Some companies are experimenting with edible coffee packaging made from materials like rice or potato starch. These packages are designed to dissolve in hot water, leaving no waste behind.
Mushroom Packaging:
Mycelium-based packaging is an innovative and sustainable option. It is made from the root systems of mushrooms and can be molded into various shapes to protect coffee beans.
Plant-Based Laminates:
Using plant-based laminates or adhesives for packaging can enhance the sustainability of traditional packaging materials like foil-lined bags.
Water-Soluble Packaging:
Water-soluble packaging materials, like PVA (polyvinyl alcohol), dissolve when exposed to water. They can be a good option for single-use coffee products like instant coffee or coffee pods.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of these materials in terms of degradability or compostability often depends on proper disposal and environmental conditions. When considering degradable materials for coffee packaging, make sure they meet relevant certification standards and communicate disposal instructions to consumers to ensure that the packaging is disposed of properly to achieve its intended environmental benefit. Additionally, check local regulations and composting facilities in your area, as their capabilities may vary.